Lichtgitter: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Seck (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Seck (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 602: | Zeile 602: | ||
Es wurden so schnell als möglich 1000 Abfragen mittels Lichtgitterkommando "read_all" (Code 0x81) im Programm lg.c gemacht. Das Kommandobyte 0x81 wird vom Lichtgitter geechot und es folgen vier binäre Datenbytes mit der Bereichsangabe des die Lichtstrahlen unterbrechenden Objektes mit Start- und Endewert. |
Es wurden so schnell als möglich 1000 Abfragen mittels Lichtgitterkommando "read_all" (Code 0x81) im Programm lg.c gemacht. Das Kommandobyte 0x81 wird vom Lichtgitter geechot und es folgen vier binäre Datenbytes mit der Bereichsangabe des die Lichtstrahlen unterbrechenden Objektes mit Start- und Endewert. |
||
Es werden also 6 Bytes übertragen. Bei einer Baudrate von 9600 ergibt das für die Zeichen bereits eine reine Übertragungszeit von 6 ms. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Für die verarbeitung im Lichtgitter und im OS9 System brucht man demzufolge 0,919 ms pro Kommandosequenz. |
|||
serio.c: |
serio.c: |
||
<source lang="c"> |
<source lang="c"> |
||
Version vom 18. Juni 2008, 11:19 Uhr
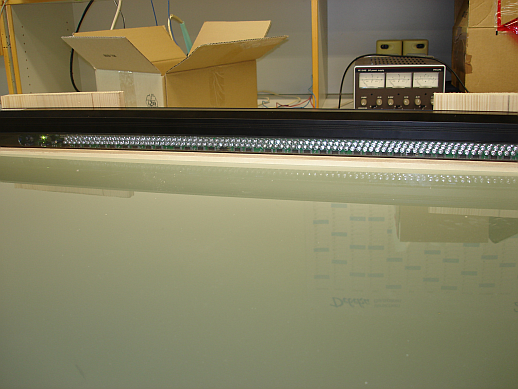
So sieht unser Leihlichtgitter der Fa. Baumer aus:
LED Sendeseite:
Empfangsseite:
folgendes ist zu beachten:
Informationen
1. FCDM082 (FCDM012 haben eine sehr grobe Auflösung)
2. Schnittstelle wählen: SSI + RS-422 oder RS-422 oder Parallel 10 Bit + RS-422
3. richtiger Ausgabewert: - erster und letzter geblockter Strahl und nicht: Standardeinstellung Anzahl der geblockten Strahlen
4. Ausgabeformat: normal (Standardeinstellung / k.A was das heisst) oder largest blocked area oder over all
5. Kodierung: Binär (Standardeinstellung) oder Gray oder BCD
6. Doppelabtastung: nein (Standardeinstellung) oder ja (erhöht die Auflösung - darüber müssen wir noch sprechen)
7. Smoothing-Wert: 1 Strahl (Standardeinstellung) bzw. ... Strahlen
8. EXTRAS Programmier-Kit - incl. Verbindungskabel und Software zum Einstellen
Wir bekommen: RS-422 + SSI Schnittstelle
Sourcecode
Ausgegeben werden für jeden Messwert:
- Zeitstempel
- Koordinate (erster oder letzter geblockter Strahl?)
- Dicke (Anzahl der geblockten Strahlen)
Fremdcode benötigt um Schnittstelle zu Verwenden!
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.h
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
#ifndef __COM_TOOLS_H__
#define __COM_TOOLS_H__
// Konstanten für Parity
#define P_NONE 0 // 0 = kein Parity Bit
#define P_EVEN 1 // 1 = gerade
#define P_ODD 2 // 2 = ungerade
#define P_SPACE 3 // 3 = immer 0
#define P_MARK 4 // 4 = immer 1
#define D_7BIT 0 // 7-Databits
#define D_8BIT 1 // 8-Databits
#define S_1BIT 0 // 1 Stopbit
#define S_1_5BIT 1 // 1.5 Stopbits
#define S_2BIT 2 // 2 Stopbits
void ComDetectPorts(int iCount,int *pMode,int iMaxPorts);
int ComInit();
int ComExit();
int ComOpen (unsigned Nr,int Baud,int Parity,int Stopbits,int Databits);
int ComClose(unsigned Nr);
int ComReadData (unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Max);
int ComRead (unsigned Nr);
int ComWriteData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Count);
int ComWrite(unsigned Nr,int Zeichen);
int ComGetReadCount (unsigned Nr);
int ComGetWriteCount(unsigned Nr);
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.cpp
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
//
// (C) Copyright Anton Zechner 2007
//
#include <windows.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include "ComTools.h"
#define MAX_COM_PORTS 8
static HANDLE hComFile[MAX_COM_PORTS];
static BOOL bIsOpen [MAX_COM_PORTS];
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComInit
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int ComInit()
{
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComExit
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int ComExit()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<MAX_COM_PORTS;i++)
{
if(!bIsOpen[i])continue;
ComClose(i);
}
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComOpen
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Öffnet eine serielle Verbindung
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Baud : Ist die Bautrate
// Parity : 0 = kein Parity Bit
// 1 = gerade
// 2 = ungerade
// 3 = immer 0
// 4 = immer 1
// Stopbits : 0 = Ein Stopbit
// 1 = Ein/einhalb Stopbits
// 2 = Zwei Stopbits
// Bits : 0 = 7 Datenbits
// 1 = 8 Datenbits
// 7 = 7 Datenbits
// 8 = 8 Datenbits
// Ergibt 1 wenn eine Schnittstelle geöffnet wurde
int ComOpen(unsigned Nr,int Baud,int Parity,int Stopbits,int Databits)
{
static const int iPMode[]={NOPARITY,EVENPARITY,ODDPARITY,SPACEPARITY,MARKPARITY};
static const int iSMode[]={ONESTOPBIT,ONE5STOPBITS,TWOSTOPBITS,ONESTOPBIT};
char cName[]="\\\\.\\COM1";
HANDLE hFile;
COMMTIMEOUTS sTo;
DCB sDcb;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
cName[7]='1'+Nr;
hFile= CreateFile(cName,GENERIC_READ|GENERIC_WRITE,0,0,OPEN_EXISTING,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,0);
if(hFile==INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
hFile=0;
return 0;
}
if(Databits==7)Databits=0;
memset(&sDcb,0,sizeof(sDcb));
sDcb.DCBlength=sizeof(sDcb);
sDcb.BaudRate = Baud;
sDcb.fParity = (Parity!=0)? TRUE:FALSE;
sDcb.fBinary = TRUE;
sDcb.Parity = iPMode[Parity];
sDcb.StopBits = iSMode[Stopbits&3];
sDcb.fOutxCtsFlow = FALSE;
sDcb.fOutxDsrFlow = FALSE;
sDcb.fDtrControl = DTR_CONTROL_ENABLE;
sDcb.fRtsControl = RTS_CONTROL_ENABLE;
sDcb.fDsrSensitivity= FALSE;
sDcb.fAbortOnError = FALSE;
sDcb.ByteSize = (Databits)? 8:7;
if(!SetCommState(hFile,&sDcb))
{
CloseHandle(hFile);
return 0;
}
sTo.ReadIntervalTimeout = MAXDWORD; // 0 ms Read-Tomeout
sTo.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 0;
sTo.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier= 12000/Baud+1; // ? ms Write timeout per byte
sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier+1;
if(!SetCommTimeouts((HANDLE)hFile,&sTo))
{
CloseHandle(hFile);
return 0;
}
hComFile[Nr]=hFile;
bIsOpen [Nr]=TRUE;
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComClose
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Schließt eine serielle Verbindung
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt 1 wenn eine Schnittstelle geschlossen wurde
int ComClose(unsigned Nr)
{
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
CloseHandle(hComFile[Nr]);
hComFile[Nr]=0;
bIsOpen [Nr]=FALSE;
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComDetectPorts
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Speichert in iCount die Anzahl der gefundenen COM Ports
// In pMode werden die Portzustänte gespeichert
// 0 = Nicht vorhanden
// 1 = Vorhanden
// 2 = Vorhanden und von einem anderen Programm benutzt
// pMode[0] für COM1
// pMode[1] für COM2
// ...
// iMaxPorts ist die Anzahl der Ports die gescannt werden.
void ComDetectPorts(int iCount,int *pMode,int iMaxPorts)
{
int i;
char cName[]="\\\\.\\COM1";
HANDLE hCom;
for(i=0;i<iMaxPorts;i++)
{
if(i<MAX_COM_PORTS && bIsOpen[i])
{
pMode[i]=1;
iCount++;
continue;
}
cName[7]='1'+i;
hCom=CreateFile(cName,GENERIC_WRITE|GENERIC_READ,0,0,OPEN_EXISTING,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,0);
if(hCom==INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
if(GetLastError()==ERROR_FILE_NOT_FOUND)
{
pMode[i]=0;
continue;
}
else{
pMode[i]=2;
iCount++;
continue;
}
}
CloseHandle(hCom);
pMode[i]=1;
iCount++;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComRead
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ein Zeichen lesen
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt -1 wenn nichts gelesen wurde sonst das Zeichen
int ComRead(unsigned Nr)
{
unsigned char c;
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return -1;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return -1;
if(!ReadFile(hComFile[Nr],&c,1,&dwCount,0))return -1;
if(dwCount!=1)return -1;
return c;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComRead
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Mehrere Zeichen lesen
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Buffer : Buffer in dem die Zeichen gespeichert werden
// Max : Maximale Anzahl der zu lesenden Zeichen
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gelesenen Zeichen
int ComReadData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Max)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
ReadFile(hComFile[Nr],Buffer,Max,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComWrite
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ein Zeichen senden
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Zeichen : Ist das Zeichen das gesendet werden soll.
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gesendeten Zeichen
int ComWrite(unsigned Nr,int Zeichen)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
WriteFile(hComFile[Nr],&Zeichen,1,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComWrite
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Mehrere Zeichen schreiben
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Buffer : Buffer in dem die Zeichen gespeichert werden
// Count : Anzahl der zu sendenden Zeichen
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gesendeten Zeichen
int ComWriteData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Count)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
WriteFile(hComFile[Nr],Buffer,Count,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComGetReadCount
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes die im Lesepuffer der Schnittstelle sind
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes im Buffer
int ComGetReadCount(unsigned Nr)
{
COMSTAT sComStat;
DWORD dwErrorFlags;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
dwErrorFlags=0;
if(!ClearCommError(hComFile[Nr], &dwErrorFlags, &sComStat))return 0;
return sComStat.cbInQue;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComGetWriteCount
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes die im Schreibpuffer der Schnittstelle sind
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes im Buffer
int ComGetWriteCount(unsigned Nr)
{
COMSTAT sComStat;
DWORD dwErrorFlags;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
dwErrorFlags=0;
if(!ClearCommError(hComFile[Nr], &dwErrorFlags, &sComStat))return 0;
return sComStat.cbOutQue;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* spider.c
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "ComTools.h"
#define OVECCOUNT 30 /* should be a multiple of 3 */
int
spiderReadData(unsigned int port, unsigned char *data, unsigned int max)
{
return ComReadData(port, data, max);
}
/*
* Open the serial port and set the options as needed
*/
int
spiderOpenPort(unsigned int port)
{
if(!ComOpen(port,38400,1,0,8)) {
printf("spiderOpenPort failed for port 0x%x\n", port);
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
/*
* Send command to COM_PORT port and wait until the echo occurs
*/
int
spiderSendCommand(unsigned int port, unsigned int command)
{
if (ComWrite(port, command) == -1) {
printf("spiderSendCommand failed for write on port 0x%x command 0x%x\n",
port, command);
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
/* wait until data is available */
while (!ComGetReadCount(port)) {
}
if (ComRead(port) != command) {
printf("spiderSendCommand failed for read on port 0x%x command 0x%x\n",
port, command);
return -1;
}
return command;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.cpp
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
//
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <string.h>
#define COM_PORT 1
#define OVECCOUNT 30 /* should be a multiple of 3 */
int
outputData(unsigned char *data, unsigned int max)
{
int i = 0;
printf("0x%.2x%.2x\t", data[1] & 0xff, data[0] & 0xff);
printf("0x%.2x%.2x\n", data[3] & 0xff, data[2]) & 0xff;
return 0;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* main
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned char data[4];
unsigned int res = 0;
unsigned int i = 0;
SYSTEMTIME stime, atime;
//open serial terminal port
printf("spiderOpenPort(): 0x%x\n", spiderOpenPort(COM_PORT));
GetSystemTime(&stime);
for (i = 0; i < 150; i++) {
//send read_all command
//printf("spiderSendCommand(): 0x%x\n",0);
spiderSendCommand(COM_PORT, 0x81);
//read data
res = spiderReadData(COM_PORT, data, sizeof(data));
//printf("spiderReadData(): 0x%x\n", res);
GetSystemTime(&atime);
printf("%d\t%ul\t", i, (atime.wMilliseconds + atime.wSecond * 1000) -
(stime.wMilliseconds + stime.wSecond * 1000));
outputData(data, res);
}
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
OS9 Testmessung
Die Testmessungen mit dem Lichtgitter wurde auf einem OS9-Rechner mit PowerPC 555 wiederholt.
Systembedingt wurde die serielle Schnittstelle /term verwendet, die nur! mit 9600 Baud bei 1 Stopbit und even Parity, betrieben werden kann :-((
Die Schnittstelle musste zunächst in den binär-Moddus versetzt werden, damit volle 8 Bit Wertevorrat gesendet und empfangen werden kann; das erledigt das Programm serio.c.
Es wurden so schnell als möglich 1000 Abfragen mittels Lichtgitterkommando "read_all" (Code 0x81) im Programm lg.c gemacht. Das Kommandobyte 0x81 wird vom Lichtgitter geechot und es folgen vier binäre Datenbytes mit der Bereichsangabe des die Lichtstrahlen unterbrechenden Objektes mit Start- und Endewert.
Es werden also 6 Bytes übertragen. Bei einer Baudrate von 9600 ergibt das für die Zeichen bereits eine reine Übertragungszeit von 6 ms.
Es wurden 1000 Abfragen in 6919 ms geschafft.
Für die verarbeitung im Lichtgitter und im OS9 System brucht man demzufolge 0,919 ms pro Kommandosequenz. serio.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <modes.h>
#include <types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sysglob.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main (int argc, char* argv)
{
printf ("serioraw v1.0 PPC turn /term into raw mode 38kbaud even parity\n");
system("kill 5;kill 7;kill 2; kill 9");
system("xmode /term nopause noecho");
system ("xmode /term xon=0x0 xoff=0x0");
system("xmode /term abort=0x0 bell=0x0");
system("xmode /term nobsb");
system("xmode /term nodel");
system("xmode /term nobsb");
system("xmode /term eof=0x0");
system("xmode /term eor=0x0");
system("xmode /term bsp=0x0");
system("xmode /term tab=0x0");
system("xmode /term quit=0x0");
system("xmode /term noupc");
system("xmode /term 0x7f=PASSTHRU 0x01=PASSTHRU 0x02=PASSTHRU 0x03=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x04=PASSTHRU 0x05=PASSTHRU 0x06=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x08=PASSTHRU 0x09=PASSTHRU 0x0b=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x0c=PASSTHRU 0x0d=PASSTHRU 0x10=PASSTHRU 0x11=PASSTHRU 0x12=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x13=PASSTHRU 0x17=PASSTHRU 0x18=PASSTHRU 0x1a=PASSTHRU 0x1b=PASSTHRU");
system("xmode /term baud=9600 parity=even");
return 0;
}
lg.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <modes.h>
#include <types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sysglob.h>
#include <sg_codes.h>
u_int32 myclock(void)
{
glob_buff myg;
_os_getsys (offsetof(sysglobs, d_ticks ),sizeof(u_int32),&myg);
return myg.lng;
}
u_int32 wr_cmd(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd)
{
u_int32 count;
error_code ierr;
count=1;
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count);
count=0;
_os_gs_ready(pd,&count);
count=1;
_os_read(pd,&cmd,&count);
return cmd;
}
u_int32 wr_dat(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd)
{
u_int32 count;
error_code ierr;
count=1;
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count);
return cmd;
}
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
char buf;
path_id path;
u_int32 count,icount,tstart,tend;
error_code ierr;
unsigned char cmd;
unsigned char data[100];
printf("Lichtgittertestprog V1.0 R.Seck\n");
/* stoppen aller aAktivitäten auf /term und baud=38400*/
ierr=_os_open("/term",S_IWRITE|S_IREAD,&path);
_os_gs_ready(path,&count);
if (count!=0) _os_read(path,&data,&count);
wr_cmd(path,0x00);
wr_cmd(path,0x89); /* read DATA und POS*/
wr_dat(path,0x8f); /* read DATA und POS*/
tstart=myclock();
for (icount=1;icount<1000;icount++) {
wr_cmd(path,0x81); /* read DATA und POS*/
_os_gs_ready(path,&count);
count=4;
_os_read(path,&data,&count);
}
tend=myclock();
printf("Lichtgitterzyclus: %d [ms] 1000 Messungen gelesen\n",tend-tstart);
_os_close (path);
return 0;
}