Lichtgitter: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Seck (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Seck (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (9 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
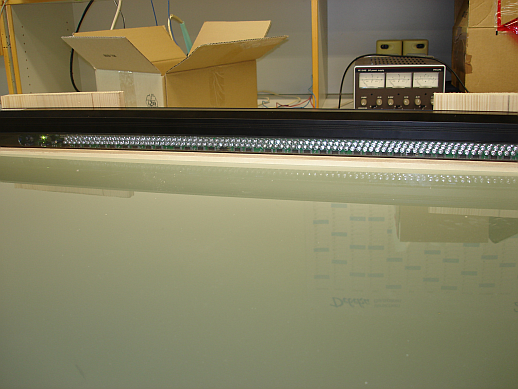
So sieht unser Leihlichtgitter der Fa. Baumer aus: |
So sieht unser Leihlichtgitter der Fa. Baumer aus: |
||
LED Sendeseite: |
|||
[[Bild:Lichtgitter.jpg]] |
|||
[[Bild:Lichtgitter1.png]] |
|||
Empfangsseite: |
|||
[[Bild:Lichtgitter2.png]] |
|||
folgendes ist zu beachten: |
folgendes ist zu beachten: |
||
| Zeile 583: | Zeile 588: | ||
} |
} |
||
</source> |
|||
== '''OS9 Testmessung''' == |
|||
Die Testmessungen mit dem Lichtgitter wurde auf einem OS9-Rechner mit PowerPC 555 wiederholt. |
|||
Systembedingt wurde die serielle Schnittstelle /term verwendet, die nur! mit 9600 Baud bei 1 Stopbit und even Parity, betrieben werden kann :-(( |
|||
Die Schnittstelle musste zunächst in den binär-Moddus versetzt werden, damit volle 8 Bit Wertevorrat gesendet und empfangen werden kann; das erledigt das Programm serio.c. |
|||
Es wurden so schnell als möglich 1000 Abfragen mittels Lichtgitterkommando "read_all" (Code 0x81) im Programm lg.c gemacht. Das Kommandobyte 0x81 wird vom Lichtgitter geechot und es folgen vier binäre Datenbytes mit der Bereichsangabe des die Lichtstrahlen unterbrechenden Objektes mit Start- und Endewert. |
|||
Es werden also 6 Bytes übertragen. Bei einer Baudrate von 9600 ergibt das für die Zeichen bereits eine reine Übertragungszeit von 6 ms. |
|||
Für die Verarbeitung im Lichtgitter und im OS9 System braucht man demzufolge 0,919 ms pro Kommandosequenz. |
|||
Die minimale erreichbar Zykluszeit des Lichtgitters ist mit ca. 5,5 ms angegeben bei 38400 Baud Übertragungsrate. |
|||
== '''Es wurden 1000 Abfragen in 6919 ms geschafft.''' == |
|||
serio.c: |
|||
<source lang="c"> |
|||
#include <stdio.h> |
|||
#include <stddef.h> |
|||
#include <modes.h> |
|||
#include <types.h> |
|||
#include <stdlib.h> |
|||
#include <sysglob.h> |
|||
#include <stdio.h> |
|||
#include <stdlib.h> |
|||
int main (int argc, char* argv) |
|||
{ |
|||
printf ("serioraw v1.0 PPC turn /term into raw mode 38kbaud even parity\n"); |
|||
system("kill 5;kill 7;kill 2; kill 9"); |
|||
system("xmode /term nopause noecho"); |
|||
system ("xmode /term xon=0x0 xoff=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term abort=0x0 bell=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term nobsb"); |
|||
system("xmode /term nodel"); |
|||
system("xmode /term nobsb"); |
|||
system("xmode /term eof=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term eor=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term bsp=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term tab=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term quit=0x0"); |
|||
system("xmode /term noupc"); |
|||
system("xmode /term 0x7f=PASSTHRU 0x01=PASSTHRU 0x02=PASSTHRU 0x03=PASSTHRU "); |
|||
system("xmode /term 0x04=PASSTHRU 0x05=PASSTHRU 0x06=PASSTHRU "); |
|||
system("xmode /term 0x08=PASSTHRU 0x09=PASSTHRU 0x0b=PASSTHRU "); |
|||
system("xmode /term 0x0c=PASSTHRU 0x0d=PASSTHRU 0x10=PASSTHRU 0x11=PASSTHRU 0x12=PASSTHRU "); |
|||
system("xmode /term 0x13=PASSTHRU 0x17=PASSTHRU 0x18=PASSTHRU 0x1a=PASSTHRU 0x1b=PASSTHRU"); |
|||
system("xmode /term baud=9600 parity=even"); |
|||
return 0; |
|||
} |
|||
</source> |
|||
lg.c: |
|||
<source lang="c"> |
|||
#include <stdio.h> |
|||
#include <stddef.h> |
|||
#include <modes.h> |
|||
#include <types.h> |
|||
#include <stdlib.h> |
|||
#include <sysglob.h> |
|||
#include <sg_codes.h> |
|||
u_int32 myclock(void) |
|||
{ |
|||
glob_buff myg; |
|||
_os_getsys (offsetof(sysglobs, d_ticks ),sizeof(u_int32),&myg); |
|||
return myg.lng; |
|||
} |
|||
u_int32 wr_cmd(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd) |
|||
{ |
|||
u_int32 count; |
|||
error_code ierr; |
|||
count=1; |
|||
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count); |
|||
count=0; |
|||
_os_gs_ready(pd,&count); |
|||
count=1; |
|||
_os_read(pd,&cmd,&count); |
|||
return cmd; |
|||
} |
|||
u_int32 wr_dat(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd) |
|||
{ |
|||
u_int32 count; |
|||
error_code ierr; |
|||
count=1; |
|||
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count); |
|||
return cmd; |
|||
} |
|||
int main (int argc, char** argv) |
|||
{ |
|||
char buf; |
|||
path_id path; |
|||
u_int32 count,icount,tstart,tend; |
|||
error_code ierr; |
|||
unsigned char cmd; |
|||
unsigned char data[100]; |
|||
printf("Lichtgittertestprog V1.0 R.Seck\n"); |
|||
/* stoppen aller aAktivitäten auf /term und baud=38400*/ |
|||
ierr=_os_open("/term",S_IWRITE|S_IREAD,&path); |
|||
_os_gs_ready(path,&count); |
|||
if (count!=0) _os_read(path,&data,&count); |
|||
wr_cmd(path,0x00); |
|||
wr_cmd(path,0x89); /* read DATA und POS*/ |
|||
wr_dat(path,0x8f); /* read DATA und POS*/ |
|||
tstart=myclock(); |
|||
for (icount=1;icount<1000;icount++) { |
|||
wr_cmd(path,0x81); /* read DATA und POS*/ |
|||
_os_gs_ready(path,&count); |
|||
count=4; |
|||
_os_read(path,&data,&count); |
|||
} |
|||
tend=myclock(); |
|||
printf("Lichtgitterzyclus: %d [ms] 1000 Messungen gelesen\n",tend-tstart); |
|||
_os_close (path); |
|||
return 0; |
|||
} |
|||
</source> |
</source> |
||
Aktuelle Version vom 18. Juni 2008, 11:22 Uhr
So sieht unser Leihlichtgitter der Fa. Baumer aus:
LED Sendeseite:
Empfangsseite:
folgendes ist zu beachten:
Informationen
1. FCDM082 (FCDM012 haben eine sehr grobe Auflösung)
2. Schnittstelle wählen: SSI + RS-422 oder RS-422 oder Parallel 10 Bit + RS-422
3. richtiger Ausgabewert: - erster und letzter geblockter Strahl und nicht: Standardeinstellung Anzahl der geblockten Strahlen
4. Ausgabeformat: normal (Standardeinstellung / k.A was das heisst) oder largest blocked area oder over all
5. Kodierung: Binär (Standardeinstellung) oder Gray oder BCD
6. Doppelabtastung: nein (Standardeinstellung) oder ja (erhöht die Auflösung - darüber müssen wir noch sprechen)
7. Smoothing-Wert: 1 Strahl (Standardeinstellung) bzw. ... Strahlen
8. EXTRAS Programmier-Kit - incl. Verbindungskabel und Software zum Einstellen
Wir bekommen: RS-422 + SSI Schnittstelle
Sourcecode
Ausgegeben werden für jeden Messwert:
- Zeitstempel
- Koordinate (erster oder letzter geblockter Strahl?)
- Dicke (Anzahl der geblockten Strahlen)
Fremdcode benötigt um Schnittstelle zu Verwenden!
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.h
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
#ifndef __COM_TOOLS_H__
#define __COM_TOOLS_H__
// Konstanten für Parity
#define P_NONE 0 // 0 = kein Parity Bit
#define P_EVEN 1 // 1 = gerade
#define P_ODD 2 // 2 = ungerade
#define P_SPACE 3 // 3 = immer 0
#define P_MARK 4 // 4 = immer 1
#define D_7BIT 0 // 7-Databits
#define D_8BIT 1 // 8-Databits
#define S_1BIT 0 // 1 Stopbit
#define S_1_5BIT 1 // 1.5 Stopbits
#define S_2BIT 2 // 2 Stopbits
void ComDetectPorts(int iCount,int *pMode,int iMaxPorts);
int ComInit();
int ComExit();
int ComOpen (unsigned Nr,int Baud,int Parity,int Stopbits,int Databits);
int ComClose(unsigned Nr);
int ComReadData (unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Max);
int ComRead (unsigned Nr);
int ComWriteData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Count);
int ComWrite(unsigned Nr,int Zeichen);
int ComGetReadCount (unsigned Nr);
int ComGetWriteCount(unsigned Nr);
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.cpp
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
//
// (C) Copyright Anton Zechner 2007
//
#include <windows.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include "ComTools.h"
#define MAX_COM_PORTS 8
static HANDLE hComFile[MAX_COM_PORTS];
static BOOL bIsOpen [MAX_COM_PORTS];
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComInit
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int ComInit()
{
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComExit
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int ComExit()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<MAX_COM_PORTS;i++)
{
if(!bIsOpen[i])continue;
ComClose(i);
}
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComOpen
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Öffnet eine serielle Verbindung
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Baud : Ist die Bautrate
// Parity : 0 = kein Parity Bit
// 1 = gerade
// 2 = ungerade
// 3 = immer 0
// 4 = immer 1
// Stopbits : 0 = Ein Stopbit
// 1 = Ein/einhalb Stopbits
// 2 = Zwei Stopbits
// Bits : 0 = 7 Datenbits
// 1 = 8 Datenbits
// 7 = 7 Datenbits
// 8 = 8 Datenbits
// Ergibt 1 wenn eine Schnittstelle geöffnet wurde
int ComOpen(unsigned Nr,int Baud,int Parity,int Stopbits,int Databits)
{
static const int iPMode[]={NOPARITY,EVENPARITY,ODDPARITY,SPACEPARITY,MARKPARITY};
static const int iSMode[]={ONESTOPBIT,ONE5STOPBITS,TWOSTOPBITS,ONESTOPBIT};
char cName[]="\\\\.\\COM1";
HANDLE hFile;
COMMTIMEOUTS sTo;
DCB sDcb;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
cName[7]='1'+Nr;
hFile= CreateFile(cName,GENERIC_READ|GENERIC_WRITE,0,0,OPEN_EXISTING,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,0);
if(hFile==INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
hFile=0;
return 0;
}
if(Databits==7)Databits=0;
memset(&sDcb,0,sizeof(sDcb));
sDcb.DCBlength=sizeof(sDcb);
sDcb.BaudRate = Baud;
sDcb.fParity = (Parity!=0)? TRUE:FALSE;
sDcb.fBinary = TRUE;
sDcb.Parity = iPMode[Parity];
sDcb.StopBits = iSMode[Stopbits&3];
sDcb.fOutxCtsFlow = FALSE;
sDcb.fOutxDsrFlow = FALSE;
sDcb.fDtrControl = DTR_CONTROL_ENABLE;
sDcb.fRtsControl = RTS_CONTROL_ENABLE;
sDcb.fDsrSensitivity= FALSE;
sDcb.fAbortOnError = FALSE;
sDcb.ByteSize = (Databits)? 8:7;
if(!SetCommState(hFile,&sDcb))
{
CloseHandle(hFile);
return 0;
}
sTo.ReadIntervalTimeout = MAXDWORD; // 0 ms Read-Tomeout
sTo.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 0;
sTo.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier= 12000/Baud+1; // ? ms Write timeout per byte
sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = sTo.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier+1;
if(!SetCommTimeouts((HANDLE)hFile,&sTo))
{
CloseHandle(hFile);
return 0;
}
hComFile[Nr]=hFile;
bIsOpen [Nr]=TRUE;
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComClose
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Schließt eine serielle Verbindung
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt 1 wenn eine Schnittstelle geschlossen wurde
int ComClose(unsigned Nr)
{
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
CloseHandle(hComFile[Nr]);
hComFile[Nr]=0;
bIsOpen [Nr]=FALSE;
return 1;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComDetectPorts
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Speichert in iCount die Anzahl der gefundenen COM Ports
// In pMode werden die Portzustänte gespeichert
// 0 = Nicht vorhanden
// 1 = Vorhanden
// 2 = Vorhanden und von einem anderen Programm benutzt
// pMode[0] für COM1
// pMode[1] für COM2
// ...
// iMaxPorts ist die Anzahl der Ports die gescannt werden.
void ComDetectPorts(int iCount,int *pMode,int iMaxPorts)
{
int i;
char cName[]="\\\\.\\COM1";
HANDLE hCom;
for(i=0;i<iMaxPorts;i++)
{
if(i<MAX_COM_PORTS && bIsOpen[i])
{
pMode[i]=1;
iCount++;
continue;
}
cName[7]='1'+i;
hCom=CreateFile(cName,GENERIC_WRITE|GENERIC_READ,0,0,OPEN_EXISTING,FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,0);
if(hCom==INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
if(GetLastError()==ERROR_FILE_NOT_FOUND)
{
pMode[i]=0;
continue;
}
else{
pMode[i]=2;
iCount++;
continue;
}
}
CloseHandle(hCom);
pMode[i]=1;
iCount++;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComRead
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ein Zeichen lesen
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt -1 wenn nichts gelesen wurde sonst das Zeichen
int ComRead(unsigned Nr)
{
unsigned char c;
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return -1;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return -1;
if(!ReadFile(hComFile[Nr],&c,1,&dwCount,0))return -1;
if(dwCount!=1)return -1;
return c;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComRead
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Mehrere Zeichen lesen
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Buffer : Buffer in dem die Zeichen gespeichert werden
// Max : Maximale Anzahl der zu lesenden Zeichen
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gelesenen Zeichen
int ComReadData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Max)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
ReadFile(hComFile[Nr],Buffer,Max,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComWrite
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ein Zeichen senden
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Zeichen : Ist das Zeichen das gesendet werden soll.
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gesendeten Zeichen
int ComWrite(unsigned Nr,int Zeichen)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
WriteFile(hComFile[Nr],&Zeichen,1,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComWrite
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Mehrere Zeichen schreiben
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Buffer : Buffer in dem die Zeichen gespeichert werden
// Count : Anzahl der zu sendenden Zeichen
// Ergibt die Anzahl der gesendeten Zeichen
int ComWriteData(unsigned Nr,void *Buffer,int Count)
{
DWORD dwCount;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
WriteFile(hComFile[Nr],Buffer,Count,&dwCount,0);
return dwCount;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComGetReadCount
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes die im Lesepuffer der Schnittstelle sind
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes im Buffer
int ComGetReadCount(unsigned Nr)
{
COMSTAT sComStat;
DWORD dwErrorFlags;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
dwErrorFlags=0;
if(!ClearCommError(hComFile[Nr], &dwErrorFlags, &sComStat))return 0;
return sComStat.cbInQue;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* ComGetWriteCount
//*
//*****************************************************************************
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes die im Schreibpuffer der Schnittstelle sind
// Nr : Ist die Nummer des Com-Ports (0=COM1 1=COM2 ...)
// Ergibt die Anzahl der Bytes im Buffer
int ComGetWriteCount(unsigned Nr)
{
COMSTAT sComStat;
DWORD dwErrorFlags;
if(Nr>=MAX_COM_PORTS)return 0;
if(!bIsOpen[Nr])return 0;
dwErrorFlags=0;
if(!ClearCommError(hComFile[Nr], &dwErrorFlags, &sComStat))return 0;
return sComStat.cbOutQue;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* spider.c
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "ComTools.h"
#define OVECCOUNT 30 /* should be a multiple of 3 */
int
spiderReadData(unsigned int port, unsigned char *data, unsigned int max)
{
return ComReadData(port, data, max);
}
/*
* Open the serial port and set the options as needed
*/
int
spiderOpenPort(unsigned int port)
{
if(!ComOpen(port,38400,1,0,8)) {
printf("spiderOpenPort failed for port 0x%x\n", port);
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
/*
* Send command to COM_PORT port and wait until the echo occurs
*/
int
spiderSendCommand(unsigned int port, unsigned int command)
{
if (ComWrite(port, command) == -1) {
printf("spiderSendCommand failed for write on port 0x%x command 0x%x\n",
port, command);
return -1;
}
sleep(1);
/* wait until data is available */
while (!ComGetReadCount(port)) {
}
if (ComRead(port) != command) {
printf("spiderSendCommand failed for read on port 0x%x command 0x%x\n",
port, command);
return -1;
}
return command;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//*
//* ComTools.cpp
//*
//*
//*****************************************************************************
//
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <string.h>
#define COM_PORT 1
#define OVECCOUNT 30 /* should be a multiple of 3 */
int
outputData(unsigned char *data, unsigned int max)
{
int i = 0;
printf("0x%.2x%.2x\t", data[1] & 0xff, data[0] & 0xff);
printf("0x%.2x%.2x\n", data[3] & 0xff, data[2]) & 0xff;
return 0;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//*
//* main
//*
//*****************************************************************************
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned char data[4];
unsigned int res = 0;
unsigned int i = 0;
SYSTEMTIME stime, atime;
//open serial terminal port
printf("spiderOpenPort(): 0x%x\n", spiderOpenPort(COM_PORT));
GetSystemTime(&stime);
for (i = 0; i < 150; i++) {
//send read_all command
//printf("spiderSendCommand(): 0x%x\n",0);
spiderSendCommand(COM_PORT, 0x81);
//read data
res = spiderReadData(COM_PORT, data, sizeof(data));
//printf("spiderReadData(): 0x%x\n", res);
GetSystemTime(&atime);
printf("%d\t%ul\t", i, (atime.wMilliseconds + atime.wSecond * 1000) -
(stime.wMilliseconds + stime.wSecond * 1000));
outputData(data, res);
}
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
OS9 Testmessung
Die Testmessungen mit dem Lichtgitter wurde auf einem OS9-Rechner mit PowerPC 555 wiederholt.
Systembedingt wurde die serielle Schnittstelle /term verwendet, die nur! mit 9600 Baud bei 1 Stopbit und even Parity, betrieben werden kann :-((
Die Schnittstelle musste zunächst in den binär-Moddus versetzt werden, damit volle 8 Bit Wertevorrat gesendet und empfangen werden kann; das erledigt das Programm serio.c.
Es wurden so schnell als möglich 1000 Abfragen mittels Lichtgitterkommando "read_all" (Code 0x81) im Programm lg.c gemacht. Das Kommandobyte 0x81 wird vom Lichtgitter geechot und es folgen vier binäre Datenbytes mit der Bereichsangabe des die Lichtstrahlen unterbrechenden Objektes mit Start- und Endewert.
Es werden also 6 Bytes übertragen. Bei einer Baudrate von 9600 ergibt das für die Zeichen bereits eine reine Übertragungszeit von 6 ms. Für die Verarbeitung im Lichtgitter und im OS9 System braucht man demzufolge 0,919 ms pro Kommandosequenz. Die minimale erreichbar Zykluszeit des Lichtgitters ist mit ca. 5,5 ms angegeben bei 38400 Baud Übertragungsrate.
Es wurden 1000 Abfragen in 6919 ms geschafft.
serio.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <modes.h>
#include <types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sysglob.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main (int argc, char* argv)
{
printf ("serioraw v1.0 PPC turn /term into raw mode 38kbaud even parity\n");
system("kill 5;kill 7;kill 2; kill 9");
system("xmode /term nopause noecho");
system ("xmode /term xon=0x0 xoff=0x0");
system("xmode /term abort=0x0 bell=0x0");
system("xmode /term nobsb");
system("xmode /term nodel");
system("xmode /term nobsb");
system("xmode /term eof=0x0");
system("xmode /term eor=0x0");
system("xmode /term bsp=0x0");
system("xmode /term tab=0x0");
system("xmode /term quit=0x0");
system("xmode /term noupc");
system("xmode /term 0x7f=PASSTHRU 0x01=PASSTHRU 0x02=PASSTHRU 0x03=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x04=PASSTHRU 0x05=PASSTHRU 0x06=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x08=PASSTHRU 0x09=PASSTHRU 0x0b=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x0c=PASSTHRU 0x0d=PASSTHRU 0x10=PASSTHRU 0x11=PASSTHRU 0x12=PASSTHRU ");
system("xmode /term 0x13=PASSTHRU 0x17=PASSTHRU 0x18=PASSTHRU 0x1a=PASSTHRU 0x1b=PASSTHRU");
system("xmode /term baud=9600 parity=even");
return 0;
}
lg.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <modes.h>
#include <types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sysglob.h>
#include <sg_codes.h>
u_int32 myclock(void)
{
glob_buff myg;
_os_getsys (offsetof(sysglobs, d_ticks ),sizeof(u_int32),&myg);
return myg.lng;
}
u_int32 wr_cmd(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd)
{
u_int32 count;
error_code ierr;
count=1;
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count);
count=0;
_os_gs_ready(pd,&count);
count=1;
_os_read(pd,&cmd,&count);
return cmd;
}
u_int32 wr_dat(path_id pd,u_int8 cmd)
{
u_int32 count;
error_code ierr;
count=1;
_os_write(pd,&cmd,&count);
return cmd;
}
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
char buf;
path_id path;
u_int32 count,icount,tstart,tend;
error_code ierr;
unsigned char cmd;
unsigned char data[100];
printf("Lichtgittertestprog V1.0 R.Seck\n");
/* stoppen aller aAktivitäten auf /term und baud=38400*/
ierr=_os_open("/term",S_IWRITE|S_IREAD,&path);
_os_gs_ready(path,&count);
if (count!=0) _os_read(path,&data,&count);
wr_cmd(path,0x00);
wr_cmd(path,0x89); /* read DATA und POS*/
wr_dat(path,0x8f); /* read DATA und POS*/
tstart=myclock();
for (icount=1;icount<1000;icount++) {
wr_cmd(path,0x81); /* read DATA und POS*/
_os_gs_ready(path,&count);
count=4;
_os_read(path,&data,&count);
}
tend=myclock();
printf("Lichtgitterzyclus: %d [ms] 1000 Messungen gelesen\n",tend-tstart);
_os_close (path);
return 0;
}